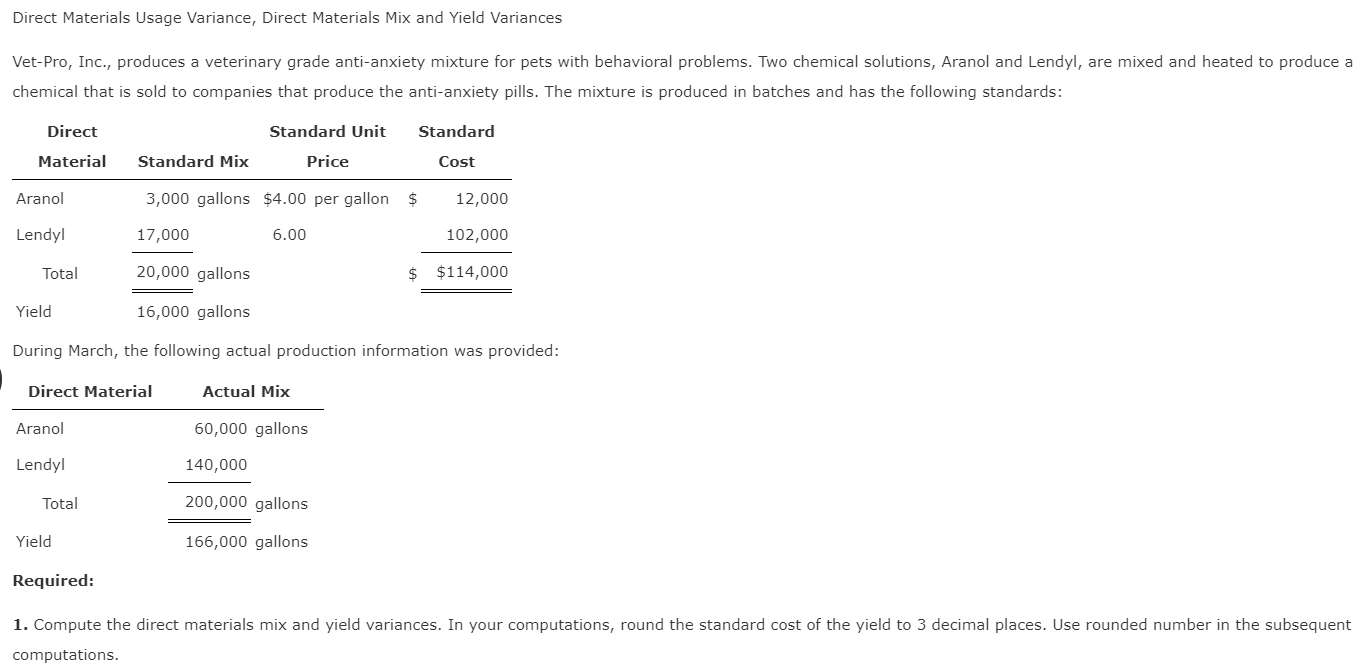
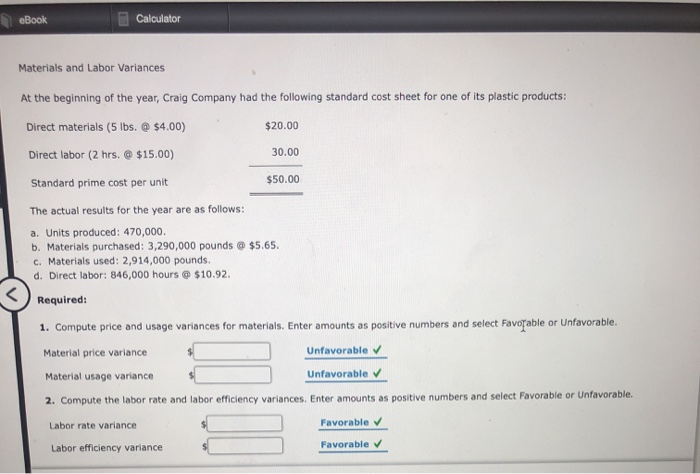
Direct labor rate variance arise from the difference in actual pay rate of laborers versus what is budgeted. Actual labor costs may differ from budgeted costs due to differences in rate and efficiency. If the total actual cost incurred is less than the total standard cost, the variance is favorable.
- In this illustration, AH is the actual hours worked, AR is the actual labor rate per hour, SR is the standard labor rate per hour, and SH is the standard hours for the output achieved.
- Figure 10.43 shows the connection between the direct labor rate variance and direct labor time variance to total direct labor variance.
- Since this measures the performance of workers, it may be caused by worker deficiencies or by poor production methods.
- On the other hand, it is possible that the company’s productive efficiency drove the variances (a variable overhead efficiency variance).
- The process begins with establishing standard labor costs, which are derived from historical data, industry benchmarks, and internal performance metrics.
Ask a Financial Professional Any Question
For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. After filing for Chapter 11 bankruptcy inDecember 2002, United cut close to $5,000,000,000in annual expenditures. As a result of these cost cuts, United wasable to emerge from bankruptcy in 2006. A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation. Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise. Ask a question about your financial situation providing as much detail as possible.
Standard Costing Outline
Conversely, a less experienced workforce may require more time and supervision, resulting in unfavorable variances. Investing in continuous training and development can help mitigate these discrepancies by enhancing employee competencies. Another significant component is labor efficiency variance, which measures the difference between the expected hours of labor required to produce a certain level of output and the actual hours worked. This variance retained earnings formula can be influenced by factors such as employee productivity, the effectiveness of training programs, and the efficiency of production processes. For instance, if workers complete tasks faster than anticipated due to improved skills or better tools, the labor efficiency variance will be favorable. The other two variances that are generally computed for direct labor cost are the direct labor efficiency variance and direct labor yield variance.
Which of these is most important for your financial advisor to have?
One must consider the circumstances under which the variances resulted and the materiality of amounts involved. One should also understand that not all unfavorable variances are bad. For example, buying raw materials of superior quality (at higher than anticipated prices) may be offset by reduction in waste and spoilage.
To calculate Direct Labor Mix Variance you must first identify the exact amount of labor it requires to produce a product. Figure 10.7 contains some possible explanations for the laborrate variance (left panel) and labor efficiency variance (rightpanel). In closing this discussion of standards and variances, be mindful that care should be taken in examining variances. If the original standards are not accurate and fair, the resulting variance signals will themselves prove quite misleading. Organizations can use DLYV to identify cost-saving opportunities, measure the productivity of their labor force, and improve operational efficiency.
In this question, the Bright Company has experienced a favorable labor rate variance of $45 because it has paid a lower hourly rate ($5.40) than the standard hourly rate ($5.50). Direct Labor Yield Variance (DLYV) is a measure of the difference between actual and expected labor costs, based on the number of units produced or services provided. The labor efficiency variance calculation presented previouslyshows that 18,900 in actual hours worked is lower than the 21,000budgeted hours. Clearly, this is favorable since theactual hours worked was lower than the expected (budgeted)hours.
In this illustration, AH is the actual hours worked, AR is the actual labor rate per hour, SR is the standard labor rate per hour, and SH is the standard hours for the output achieved. The direct labor (DL) variance is the difference between the total actual direct labor cost and the total standard cost. Effective management of labor variance is crucial for maintaining a company’s financial health and operational efficiency. Labor variance, the difference between expected and actual labor costs, can significantly impact profitability and resource allocation. Usually, direct labor rate variance does not occur due to change in labor rates because they are normally pretty easy to predict.
Calculating DLYV is important to assess the productivity of labor and identify areas where operational efficiency can be improved. The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly. Direct Labor Mix Variance is defined as the difference between the exact amount of labor needed to manufacture a product and the actual amount of labor used for that product.




